Managed systems
Bravura Privilege manages local administrative credentials and groups for workstations and servers. In the context of Bravura Privilege , these systems are referred to as managed systems .
The following sections demonstrate how to:
Product administrators require appropriate privileges to access the privileged access areas of the Manage the system (PSA) module; refer to User types and access rules and ensure that all product administrator access rights are correctly configured.
Before adding managed systems, ensure that you have restricted prior administrative access to accounts.
See also
Managed system policies define which accounts are managed, security settings and configuration options for member managed systems.
See Managed system policies for details.
You can configure options, including password change intervals, globally for Bravura Privilege . Policy-level settings override global settings.
See Privileged access management options for details.
Adding push mode managed systems
In push mode , Bravura Privilege performs remote password resets and other operations. This is controlled by the Privileged Access Manager Service that is installed automatically on the Bravura Privilege server.
Add a push mode managed system by:
Designating a target system as a Bravura Privilege managed system
Managing discovered systems
Adding a target system as a managed system
You can make any target system a managed system by selecting the Automatically create a Bravura Privilege managed system setting on the page.
The system is added as a managed system during the next auto discovery . The Privileged Access Manager Service uses parameters of the target system to determine which connector program to run and what credentials to use when it resets passwords for a managed system.
Click below to view a demonstration.
Managing discovered systems as push mode managed systems
To manage systems on a domain:
Configure an Active Directory target system to list all workstations or servers.
On the Target system information page, select the Discovery options tab, then select the type of systems you want to discover. Click Update to save the changes.
Run auto discovery by clicking Maintenance > Auto discovery.
Manage the discovered systems manually, or automatically by configuring import rules.
See:
Discovered Objects for more information about managing discovered systems
Adding local service mode managed systems
In local service mode , Bravura Privilege performs local password resets and other operations using software, the Local Workstation Service, that you install on the managed resource. The system is automatically registered the first time the Local Workstation Service communicates with the Bravura Privilege server. For more information about how this mode works, see Local service mode .
To add a local service mode managed system:
Download the MSI installation package and the ini file.
See Downloading the installation package for details.
Install the Local Workstation Service on the system.
See Installing local service mode software on Windows systems for details.
Allow the system to contact the Bravura Privilege to register itself as a discovered object.
Manage the discovered system, either manually, or using import rules.
Downloading the installation package
To download the installation package, from the Bravura Security Fabric main menu:
Click Manage the system > Privileged access > Local workstation service installation package.
Click Local workstation service installation package.
Click INF file download to download the
idmsetup.inffile that contains the encrypted workstation authentication key and address of the Bravura Privilege server.Click on MSI download (32-bit) or MSI download (64-bit) , depending on the system type, to download the Local Workstation Service installer. The installers are called
hipamlws-win-x86.msiandhipamlws-win-x64.msirespectively.Alternatively, you can retrieve the installation package from the addon idarchive directory.
You can now install the Local Workstation Service installation package.
Installing local service mode software on Windows systems
This section shows you how to install the Local Workstation Service on a Windows server or workstation by manually running the MSI installer that you downloaded in Downloading the installation package .
Note
Listing of accounts and groups are disabled for Local Workstation Service installed on domain controllers.
Do not install Local Workstation Service on Bravura Privilege
Bravura Privilege servers, or any server or workstation which is discoverable through psupdate and can be managed as a push system.
You can also install the software automatically. For example, use a software package distribution product like Microsoft’s System Center Configuration Manager and use the command line options or use group policy.
See Add-on installation command-line options for more information on the command-line options.
If you use workstation images you can install Local Workstation Service as described below. Disable the service by default and configure to Automatic after the image is placed on the workstation if you want to use the Local Workstation Service.
You can use a plugin to digitally sign files if required. See Digitally signing files for details.
To install the Local Workstation Service manually:
Copy the MSI and INF files that you downloaded earlier to a temporary location on the new server or workstation.
Launch the MSI.
A welcome screen appears.
Click Next .
Read and accept the license agreement.
Click Next .
Choose Typical setup type.
Clicking Custom allows you to change the install location
hipamlwsdirectory. This is not recommended.Enter the workstation authentication encryption key.
This is the authentication key that was entered when Bravura Privilege was originally installed. This should already be pre-filled if you downloaded the
idmsetup.inffile.Click Next .
Set the following parameters:
Bravura Privilege server The address and the virtual path of the Bravura Privilege CGI. This should already be pre-filled if you downloaded the
idmsetup.inffile. The format should be:https://<server>/<instance>/cgi/pamlws.exe
Change
serverto the Bravura Privilege server address andinstanceto the instance name or virtual directory name if required.Web proxy If the Local Workstation Service must contact the Bravura Privilege server through a proxy, type the proxy server address and port number in the format: <address> : <port> .
Validate server certificate Enable this checkbox if the web server on your Bravura Privilege server is running HTTPS. This is strongly recommended in a production installation to avoid information being sent over the network unencrypted.
Initial poll delay (seconds) Specify the time used to determine how long to wait before doing the initial poll to the Bravura Privilege server.
The actual wait time will be ±10% of the specified time, randomly determined in order to prevent a large number of systems contacting the Bravura Security Fabric server at the same time.
Click Advanced to set some extra options:
Disable service after installation Check this box to disable the Local Workstation Service after installation. You may want to disable it, for example, when building a system image for workstations with this service pre-installed.
By default this option is not checked.
Defer initial service startup until next system restart Check this box if you want to postpone running the Local Workstation Service until the system has been restarted. This requires that Disable service after installation to be deselected.
Re-register this workstation Enable this option if you are reinstalling the Local Workstation Service on a system that has previously had the Local Workstation Service installed on it. When enabled, this option checks if the managed system ID already exists on the Bravura Privilege server. If it exists, then the managed system uses that ID as its own.
Click Next .
The installer displays the page.
If required, enter the path of a Custom attribute file .
Click Next .
The installer displays the page.
Click Install to start the installation.
The installer begins copying files to your computer. The page appears after the Bravura Privilege features have been successfully installed.
Click Finish to exit.
The Local Workstation Service can now contact the Bravura Privilege server to register the host system as a discovered object. Once the service has contacted the server, it sends its system data and registers itself as a discovered system. The default interval for this initial registration is 300 seconds. After registration, the service periodically polls the Bravura Security Fabric to determine whether any jobs, such as password change or attribute listing, are required on the host system. Depending on the task that has been assigned, the service will contact the server at different intervals. If no tasks are assigned, the service will wait the poll time, as defined by the RES POLL INTERVAL, until it rechecks the server for tasks.
If the Local Workstation Service is unable to contact the Bravura Privilege server using the proxy server, it will attempt to poll again without connecting to the proxy server.
In local service mode, a service running locally on the managed system, connects via TLS-encrypted communication over a single outgoing port, the one port made available by the IIS web server into the Bravura Privilege nodes, by default, that port is 443. Please ensure, through either firewall, switch, proxies, tunneling or other networking configuration, that the workstations on which the Local Workstation Service is installed can connect to the Bravura Privilege server IIS.
You can capture log data on local service mode managed systems using the logutil program which is installed with the service.
Custom attribute file
You can use custom system attributes to define requirements for import rules. For local service mode systems, computer information is not stored on the Bravura Privilege server, but locally on the system itself.
The local service installer can read a custom attribute file and send information back to the server to be used by import rules as discovered system attributes. The custom attribute file must be in KVGroup format:
# KVGROUP-V2.0
"custom_attribute" "" = {
"<attribute1>" = "value1";
"<attribute2>" = "value2";
...
"<multi-valued attribute1>" "" = {
"<mv1-value1>";
"<mv1-value2>";
...
"<multi-valued attribute2>" "" = {
"<mv2-value1>";
....
};
}; For example:
# KVGROUP-V2.0
"custom_attribute" "" = {
"location" = "calgary";
"system_type" = "laptop";
"departments" "" = {
"sales";
"marketing";
};
}; There are some restrictions on what names the custom attributes may use. If any of the custom attributes are using these values, they will invalidate the attribute file and any new attributes will not be sent to the Bravura Privilege server. The attribute names such as NETBIOS, dNSHostName and failedAttempts are some examples.
Custom discovered system object attributes can be removed by setting the cust-attr-file registry entry of the local service of the workstation to an empty string.
Custom discovered system object attributes can be added by setting the cust-attr-file registry entry of the local service of the workstation to the full path name of the custom attribute file.
Integrating with McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO)
The Local Workstation Service can send properties of its installation to the McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO) via McAfee Agent. These properties include the product version, the installation path, and language version.
The server or workstation on which the Local Workstation Service will be installed must be added as a system on the ePO. Consult the McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator documentation to learn how to do this.
Supported versions of ePO include v4.6 or greater.
To install and configure Local Workstation Service to be ePO aware:
Contact support@bravurasecurity.com to obtain the
hipamlws-win.zipfile for integration with McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator.Copy over the
hipamlws-win.zipfile onto the ePO server.On the ePO console, go to Menu > Master Repository .
Click Check In Package.
In the File Path, click Browse to locate the
hipamlws-win.zipfile.Click Next .
Click Save.
Go to Menu > Policy > Client Task Catalog.
Click New Task.
In the Task Types dropdown menu, click Product Deployment.
Click OK.
Enter the task name; for example,
InstallLWS.In Products and components :
Select LocalWorkstationService from the first dropdown menu.
Select Install as the Action.
In the Command line field, specify the following arguments, each separated by a space:
Enable ePO integration:
ADDLOCAL=PAMLWS_EPO
The address of the Bravura Privilege server .
SERVER=http://<server>/<instance>/cgi/pamlws.exe
You can define other Local Workstation Service command line arguments .
Best practice
It is recommended that the installer pick the encrypted version of the AUTHKEY from the .inf file
Click Save.
Warning
Ensure that any previous installations of the Local Workstation Service is removed, or the installation will fail. Also, if the system is already discovered in the Bravura Privilege server from an existing installation, the installation will fail. If you are re-registering this system, ensure that the proper arguments are defined in the command line.
To run the Local Workstation Service installation manually using ePO:
Go to Menu > Systems section > System Tree.
Select the Systems tab (if not already redirected to this section).
Check off the systems to install the Local Workstation Service.
Click Actions > Agent > Run Client Task Now.
Select the install task you’ve previously created.
Click Run Task Now.
The Local Workstation Service installation will commence.
To run the Local Workstation Service installation immediately after adding a new system to the ePO:
Go to Menu > Policy > Client Task Assignments.
On the left menu pane, select the group in the system tree where the Local Workstation Service will be installed.
Click Actions > New Client Task Assignment.
In Task to Schedule, select the task you’ve previously created.
Click Next .
Set the Schedule type to Run immediately .
Click Save.
When new systems gets added to the ePO and the McAfee Agent is successfully installed on the system, the installation of the Local Workstation Service will run automatically.
To view the properties of the Local Workstation Service on ePO:
Go to Menu > Systems section > System Tree.
Select the system where the Local Workstation Service is installed.
Select the Products tab.
Select Local Workstation Service.
The properties of the Local Workstation Service will be displayed.
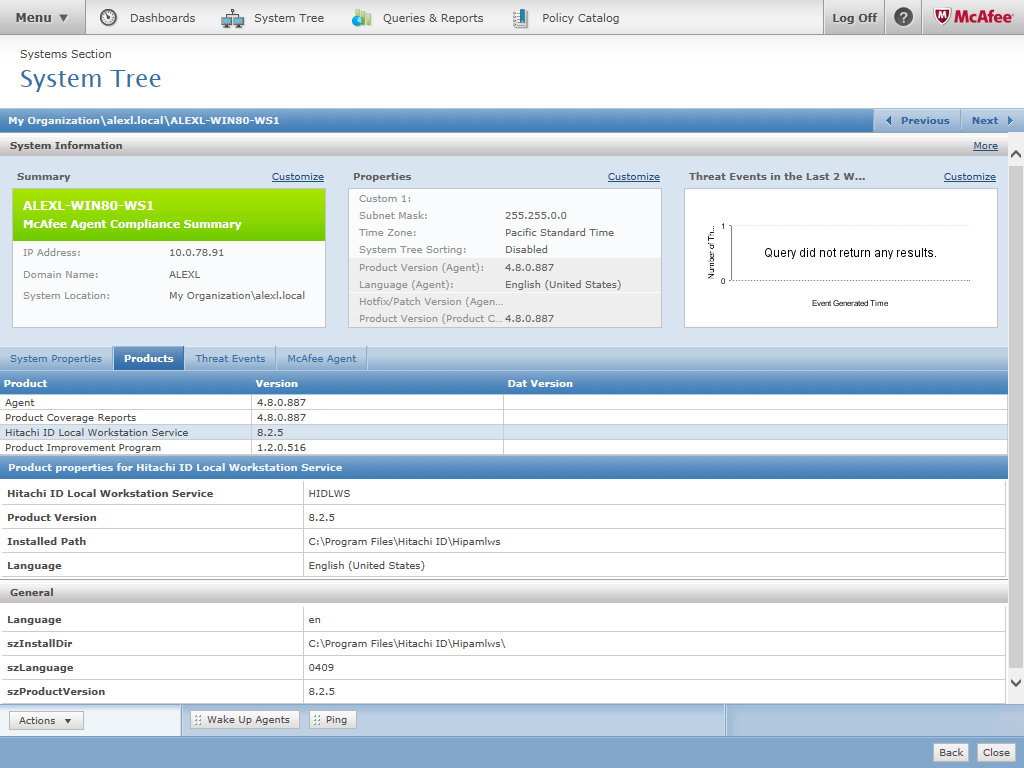
Initially, the Local Workstation Service will not show up in the list of products. You may need to wait until next time the McAfee agent sends properties to the ePO.
To uninstall the Local Workstation Service using ePO:
Go to Menu > Policy > Client Task Catalog.
Click New Task .
In the Task Types dropdown menu, click Product Deployment.
Click OK.
Enter the task name; for example,
RemoveLWS.In Products and components :
Select LocalWorkstationService from the first dropdown menu.
Select Remove as the Action.
Click Save.
Go to Menu > Systems section > System Tree.
Select Systems tab (if not already redirected to this section).
Check off the systems to remove the Local Workstation Service.
Click Actions > Agent > Run Client Task Now.
Select the uninstall task you’ve previously created.
Click Run Task Now.
The Local Workstation Service will be uninstalled.
The Local Workstation Service will be removed from the system, however this will not remove the system from the Bravura Privilege server.
Adding vault-only managed systems
In vault-only mode, Bravura Privilege simply stores information about a managed system. In this case, there is no communication between the Bravura Privilege server and the managed system; all information is inputted and maintained by product administrators. Bravura Privilege does not automatically randomize passwords for these managed systems. Vault-only managed system can only belong to vault-only type managed system policies .
You can apply access controls to allow certain users to change a stored password after they have it checked out. To do this, grant users in a user group the Randomize/Override permission to the vault-only managed system policy. See Assigning access controls to learn how to apply system policy access controls.
Product administrators require the "Create managed systems" administrative privilege in order to add a vault-only managed system.
To add a vault-only managed system:
Click Manage the system > Privileged access > Managed systems.
Click Add new…
Type an ID and Description that will be displayed to users.
Optional: Type a Help URL.
In case a longer description would help users, you can compose and post an HTML page that describes this system further, and type its URL here. Users can open the URL by clicking the managed system description text wherever the text appears as a link in the Request privileged access (PSW) module.
Click Add.
To learn how to add accounts and passwords for vault-only systems, see Storing administrative passwords manually .
Viewing and modifying managed system information
You can view managed system details on the page. Depending on how the managed system is configured, you may be able to modify some managed system information.
Only product administrators with the "Manage orphan managed systems" right can modify managed systems that are not assigned to a managed system policy .
To view or modify managed system information:
Click Manage the system > Privileged access > Managed systems.
Bravura Privilege displays a list of managed managed systems.
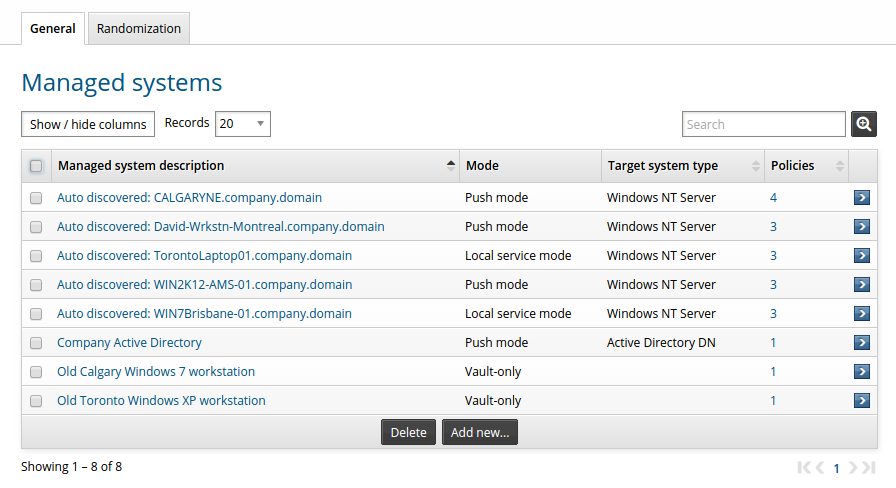
The managed system page details the managed system ’s type (local service, push, or vault-only), the target system’s type, and the number of managed system policies it belongs to. You can view if account passwords for managed systems can be randomized in the Randomization tab.
Select the managed system you want to view or modify.
Bravura Privilege displays the page.
If applicable, modify the values listed in Table 1, “Managed system options”.
Click Update.
Option | Description |
|---|---|
ID | A unique ID for the managed system. For a:
|
Description | The managed system description. For local service mode managed systems, this is automatically set using the NetBios name. It is set manually for push mode and vault-only systems. |
Address | For a push mode or local service mode managed system, this is automatically set to the target system address. This field is not available for vault-only managed systems. |
Type | The type of license the managed system should use: Workstation One workstation license allows you to manage the passwords on one workstation. Server One server license allows you to manage the passwords on one server. Application Uses one workstation license to manage the passwords on one application type managed system. Hardware Uses one workstation license to manage the passwords on one hardware type managed system. Other Uses one workstation license to manage the passwords on one other type managed system. These values are automatically assigned for push mode and local service mode managed systems. Push mode targets usually use server licenses. Local service mode managed systems depend on the system type. This field is not available for vault-only managed systems. |
OS type | The operating system or target system type. For a:
|
OS version | The operating system version or software version of your Bravura Privilege managed system. This field is not available for vault-only managed systems. |
Help URL | In case a longer description would help users, you can compose and post an HTML page that describes this system further, and type its URL here. Users can open the URL by clicking the managed system description text wherever the text appears as a link in the Request privileged access (PSW) module. |
Primary managed system policy | Indicates which managed system policy’s options to use when managing the managed system. When a managed system belongs to more than one managed system policy, you can specify which one to use. By default, this is set to the first managed system policy that the managed system becomes a member of. If that managed system policy is deleted, then the oldest remaining managed system policy is used next. Options that are applied to the managed system include: password policy, valid password change time intervals (push mode), service ID that will be used to manage the managed system (push mode), and options listed on the managed system policy’s options page. |
Last logon user | The last account that was randomized on a managed system. This applies to both push and local service mode managed systems. This field is not available for vault-only managed systems. |
Time of last successful communication | The time that the managed system last contacted the Bravura Privilege server. This applies to both push and local service mode managed systems. This field is not available for vault-only managed systems. |
Applying policies to managed systems
A managed system must belong to at least one managed system policy for users to access managed accounts or groups on the system.
To apply one or more managed systems to a managed system policy :
Click Manage the system > Privileged access > Managed systems.
Select the managed system you want to manage.
Click Policies .
Click Select… to view the list of available managed system policies.
Check the boxes next to the policies you want to assign to the managed system.
Only managed system policies matching the managed system’s mode are listed.
Click Select .
Deleting a managed system
Deleted managed systems are removed from all managed systems policies and are not placed in the HISTORICAL_DATA_GRP policy. Their passwords are no longer accessible through the GUI, but are still accessible by using KMKeyGetByAccount and RecoverKeyByAccount API functions.
Warning
Ensure that you note the password for each managed system before removing the managed system. Deleted managed systems are not placed in the HISTORICAL_DATA_GRP policy.
You cannot delete any managed system that has checked-out passwords.
To remove a managed system :
Click Manage the system > Privileged access > Managed systems.
Check the boxes for the managed systems you want to remove, and then click Delete.
Click OK to confirm your action.
If you delete a local service mode managed system, the automatically discovered object corresponding to the managed system will also be deleted.
To re-manage a push mode deleted system, the automatically discovered object corresponding to the managed system also needs to be deleted by Removing managed systems from the target system menu .
Removing managed systems from managed system policies
A managed system can also be removed or unbound from a managed system policy. In this case, if the managed system does not belong to any policy, it will be moved into the HISTORICAL_DATA_GRP policy where its passwords are stored. In this state, the passwords are still accessible, but no longer randomized.
To unbind a managed system from a managed system policy:
Click Manage the system > Privileged access > Managed system policies.
Select the managed system policy of the managed systems you want to remove.
Click Member systems.
Check the boxes for the managed systems you want to remove, and then click Delete.
Click OK to confirm your action.
Removing managed systems via the target system menu
An alternative method for deleting a managed system is through the target system menu.
Warning
Deleted managed systems are removed from all managed system policies and are not placed in the HISTORICAL_DATA_GRP policy. Their passwords are no longer accessible through the GUI.
Warning
It is strongly recommended that you back up all passwords and their password histories before deleting a target system that is a managed system.
To delete a managed system that is configured as a target system:
Click Manage the System > Resources > Target systems .
Depending on how the managed system was added, click either Manually defined or Automatically discovered.
Delete the target system by checking the boxes for systems you want to remove, then click Delete. Confirm your action.
Alternatively, unmanage the target system. Deselect the Automatically create a Privileged Access Manager managed system box for the systems you want to remove, then click Update.
If you added managed systems on an Active Directory domain automatically via auto discovery , and you removed a computer from the domain, the managed system associated is not removed during the next update, but is instead flagged as deleted. Import rules should be configured for system resolution and HISTORICAL_DATA_GRP policy assignment.
Local service mode behaviors and files
Configuration files
When the Local Workstation Service is installed on the system, it first attempts to register with the Bravura Privilege server. After it has contacted the Bravura Privilege server for the first time, it retrieves configuration settings from the Bravura Privilege server. The service saves the settings in a configuration file, hipamlwsinst.dat, in the hipamlws directory.
For more information about configuration files, see Configuration files .
Resource key
Bravura Privilege uses a key to ensure secure communication between client and server. The key allows the Bravura Privilege server to verify the identity of a local service mode managed system, and to check whether the managed system is allowed to interact with the server. It also allows the Bravura Privilege service to confirm the identity of the Bravura Privilege server. This key is negotiated and set during the installation process of the Local Workstation Service.
Bravura Privilege also uses a key to encrypt sensitive data, such as passwords, passed to the Local Workstation Service. This key is changed periodically. The number of days this key is valid for is controlled by the RESOURCE KEY CHANGE INTERVAL setting.
If this encryption key is mismatched, the Bravura Privilege will renegotiate a new key to the Local Workstation Service and the data will be resent using the new key.
Setting the resource key change interval
Set the RESOURCE KEY CHANGE INTERVAL to control the interval, in days, after which workstation keys are changed. The default is 30 days.
You can set options for each managed system policy in the Options tab. Product administrators with all administrative privileges (superuser) can set it globally in the Manage the system > Privileged access > Options menu. Group level settings override global settings. See Privileged access management options for more information.
User attribute updates on local service mode systems
Changes made to user attributes on a local service mode managed system are updated on the next poll of the Local Workstation Service. You can configure this so that some user attributes are updated less frequently than the default poll time of the Local Workstation Service.
Using a separate time interval RES ATTRIBUTE UPDATE DELAY, you can control the delay in which the user attributes will be updated. By default, the delay is set to 1440 minutes (once a day).
Only user attributes specified in RES DELAY UPDATE ATTRIBUTES are updated according to this time interval, otherwise they are updated after every poll. By default, the pwda (password age) and llogon user attributes are updated using the RES ATTRIBUTE UPDATE DELAY.
Creating administrator accounts on target systems
When adding local service mode systems using import rules, Bravura Privilege can create new credentials on the systems in order to connect.
Connection credentials are not required. Bravura Privilege can also use no credentials.
If the administrator account creation fails, Bravura Privilege logs an appropriate error message, and retries at the interval specified by RES ADMIN CREATE RETRY INTERVAL .
By default, this interval is configured for 1440 minutes. Product administrators with all administrative privileges (superuser) can set the RES ADMIN CREATE RETRY INTERVAL system variable in the Manage the system > Privileged access > Options > Managed system policies menu.
This setting allows for minimal intervention when the failure is caused by an issue on the workstation, such as a random password that fails to meet local password policy requirements. In these cases, the issue may be resolved with subsequent attempts.
If an import rule is misconfigured, for example, with an invalid security group, before attempting to create an administrator account for the first time, you may need to recreate the import rule. Some settings, such as security group, can only be set once per import rule.
See Privileged access management options for more information about global managed system policy options.
Resynchronizing a local service mode system
Registered local service mode systems resynchronize themselves by regularly re-sending their system details to the Bravura Privilege instance server. Details sent include:
User lists
User attributes
Group lists
Group memberships
Computer attributes
Resynchronization is a recovery mechanism in case the Bravura Privilege instance server is missing or has conflicting data compared to the local service mode system. Resynchronization will often be sufficient in correcting any discrepancies. In the event that resynchronization does not immediately correct discrepancies, such as database errors, it can reset the data once the source issue has been corrected.
Resynchronization is automatically triggered as configured by the RES RESYNC INTERVAL. However, you may occasionally need to resynchronize manually. To do this:
Click Manage the system > Privileged access > Managed systems.
Select the managed system you want to manage.
Click Resynchronize.
When resynchronization is running – that is, the system is in resync mode – normal operations are paused and import rules are disabled.
Resynchronization and transaction failures
The Bravura Privilege instance server will request a resynchronization when a data transaction from the local service mode system fails. Resynchronization retries will occur as required.
Resynchronization and replication failures
In a replicated environment, only one node communicates directly with local service mode systems. Resynchronization will take place as scheduled automatically or manually, and the resulting state will be replicated to other nodes.